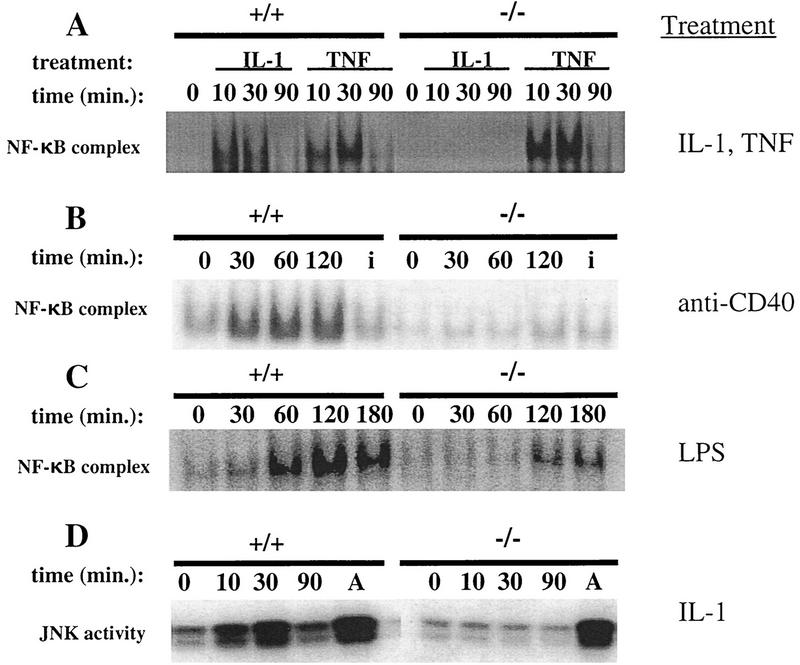
Figure 5.
NF-κB and JNK/SAPK activation in TRAF6-deficient fibroblasts and Abelson-transformed pre-B cells. (A) TRAF6−/− and wild-type EF cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml mIL-1β or mTNFα for the indicated time periods. Equivalent amounts of nuclear extract protein were incubated with a radiolabeled probe containing NF-κB binding sites. Activation of NF-κB was determined using EMSA as described in Materials and Methods. (B) NF-κB activation in response to anti-CD40. Naive splenocytes from TRAF6−/− and wild-type mice were incubated with an agonistic rat anti-mouse CD40 monoclonal antibody (5 μg/ml) or an isotype control (5 μg/ml, for 30 min) (denoted i) for the indicated time periods. Activation of NF-κB was determined as in A. Similar results were obtained using two independent TRAF6−/− and TRAF6+/+ Abelson-transformed pre-B cell lines (not shown). (C) TRAF6-deficient and wild-type Abelson-transformed pre-B cells were incubated with 20 μg/ml LPS for the indicated time points. Activation of NF-κB was determined as in A. (D) JNK/SAPK activation. TRAF6-deficient and wild-type EF cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β or 10 μg/ml anisomycin for 30 min (denoted A) for the indicated time points. Activation of SAPK/JNK was determined using a kinase assay as described in Materials and Methods.